The Riberry fruit (Syzygium luehmannii), often known as Lilly Pilly, is a glossy, small, ruby-red berry native to Australia. Revered for its tart, cranberry-like flavor with hints of spice and clove, Riberry is both a cherished bushfood and a valuable ornamental plant. In this comprehensive article, we’ll explore which country is the largest producer of Riberry fruit in the world, its cultural significance, health benefits, uses, and future prospects.
What is Riberry Fruit?
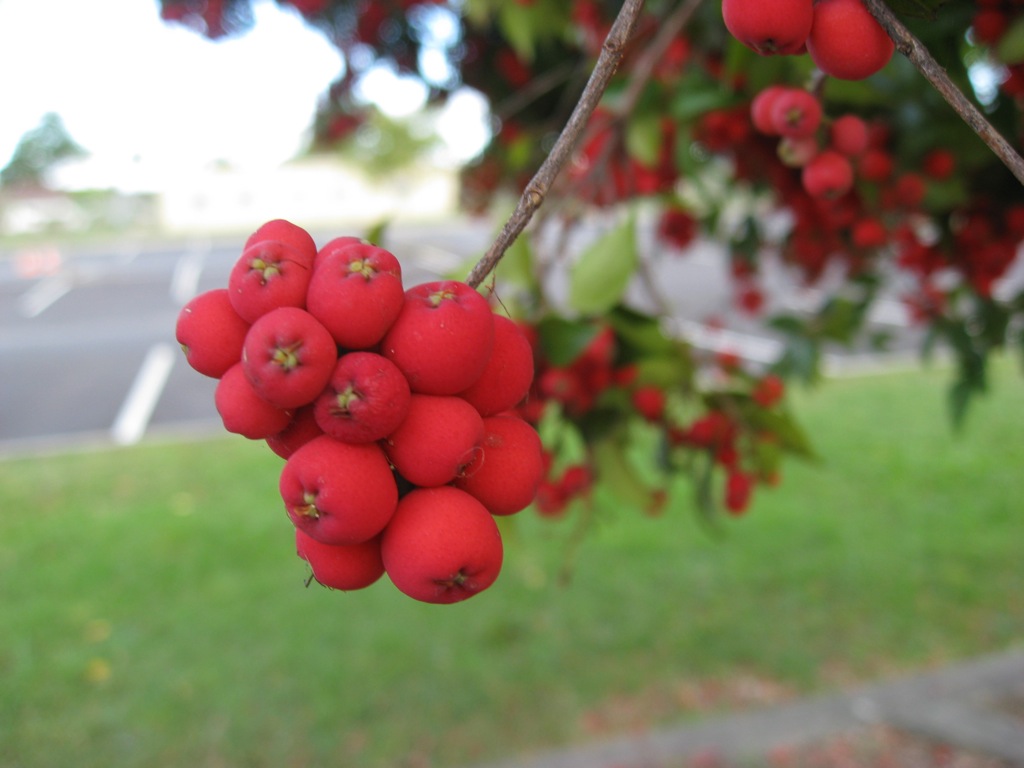

Riberry is a bright red, small elongated berry typically about 1.5–2 cm in size. The fruit grows on a tall rainforest tree indigenous to Australia, especially the coastal regions of Queensland and New South Wales.
Scientific Name: Syzygium luehmannii
Common Names: Riberry, Lilly Pilly, Small-leaved Lilly Pilly, Cherry Satinash
Historical and Cultural Importance
For centuries, Riberry has been a vital part of Australian Aboriginal bushfood culture. Indigenous communities consumed the berries fresh and used them in medicinal concoctions for sore throats and infections.
In contemporary Australia, Riberry is popular in native food movements, prized for its striking appearance, unique flavor, and culinary versatility in jams, chutneys, sauces, and desserts.
The Largest Riberry Producer in the World: Australia
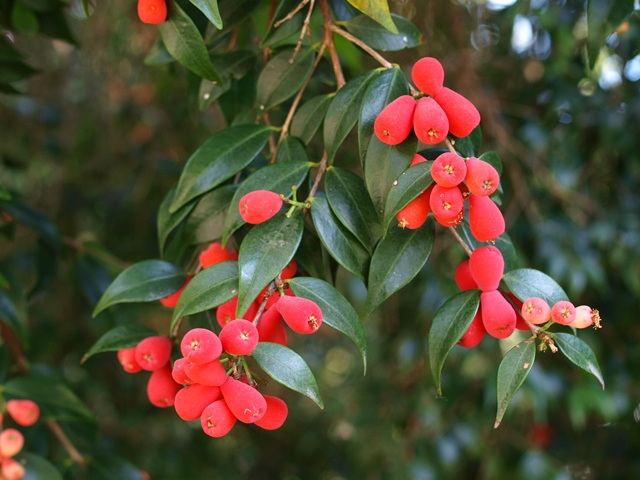

Australia holds the title as the largest Riberry fruit producer globally.
Why Australia Leads Riberry Production
1. Native Species Advantage:
Riberry trees naturally flourish in Australia’s subtropical rainforests, requiring minimal cultivation effort.
2. Aboriginal Tradition:
Centuries of indigenous knowledge about Riberry’s cultivation, foraging, and usage contribute to sustainable management.
3. Commercial Expansion:
In recent years, demand for native Australian bushfoods has driven commercial Riberry plantations, especially in Queensland and northern New South Wales.
4. Culinary Renaissance:
Australian chefs and restaurants increasingly feature Riberry in gourmet dishes, stimulating local production.
Other Riberry Growing Regions
Although native to and predominantly cultivated in Australia, Riberry trees have been introduced to select botanical gardens and experimental agroforestry projects in:
- New Zealand
- Hawaii (USA)
- Pacific Islands
However, these regions grow Riberry on a minor, non-commercial scale, mainly for ornamental and conservation purposes.
Nutritional and Health Benefits

Riberry fruit is rich in:
- Vitamin C: Enhances immune system health.
- Anthocyanins: Potent antioxidants that reduce inflammation.
- Folate and Calcium: Supports bone and cellular health.
- Natural Antimicrobials: Helps fight infections and sore throats.
Traditional medicinal uses include:
- Treating colds, coughs, and sore throats.
- Aiding digestion.
- Topical application for skin irritations.
Culinary Uses
- Fresh Consumption: Eaten raw or added to fruit salads.
- Jams and Jellies: The fruit’s tartness makes excellent preserves.
- Sauces and Chutneys: Pairs well with game meats and poultry.
- Desserts and Baked Goods: Incorporated in cakes and syrups.
- Infused Drinks: Used in cocktails, cordials, and herbal teas.
Economic Importance in Australia

Riberry plays a growing role in Australia’s native food industry:
- Bushfood Market: Riberry is a top-selling indigenous fruit.
- Commercial Plantations: Particularly in Queensland.
- Value-Added Products: Gourmet jams, sauces, and Riberry-infused spirits.
- Tourism and Events: Featured in native food festivals and farm tours.
Australia’s Riberry industry supports indigenous enterprises, small farmers, and agritourism ventures.
Challenges in Riberry Production
- Seasonal Availability: Typically harvested in summer.
- Labor-Intensive Harvest: Requires careful hand-picking.
- Perishable Nature: Fresh Riberry has a short shelf life.
- Limited Export Market: Due to perishability and niche demand.
Future Potential and Industry Trends

As interest in sustainable, local, and health-promoting superfruits grows, Riberry is poised for international recognition:
- Nutraceutical Products: High antioxidant content makes Riberry suitable for health supplements.
- Functional Foods: Incorporated into wellness drinks and probiotic yogurts.
- Export Potential: For diaspora and specialty gourmet markets.
- Agro-Tourism: Riberry farm tours and native food experiences.
Conservation and Sustainable Practices
Efforts to protect Riberry’s genetic diversity and habitat include:
- Rainforest Preservation: Safeguarding natural Riberry populations.
- Seed Banks and Nurseries: Conserving heirloom varieties.
- Indigenous-Led Enterprises: Promoting traditional knowledge and economic empowerment.
- Agroforestry Projects: Integrating Riberry into sustainable mixed cropping systems.
Conclusion
Australia’s leadership in Riberry production is both a cultural and ecological triumph. The country not only preserves the indigenous legacy of bushfoods but also adapts them to modern culinary and commercial landscapes.
While minor experimental plantings exist elsewhere, no other country approaches Australia’s scale or heritage with Riberry. Its native advantage, ideal growing conditions, and rising demand in health-conscious markets position Riberry as one of Australia’s most promising indigenous fruits.
As awareness of native superfoods expands globally, Riberry’s future in gourmet cuisine, nutraceuticals, and sustainable farming looks increasingly bright, carrying forward the traditions of Australia’s First Peoples into contemporary gastronomy and wellness trends.




Leave A Comment