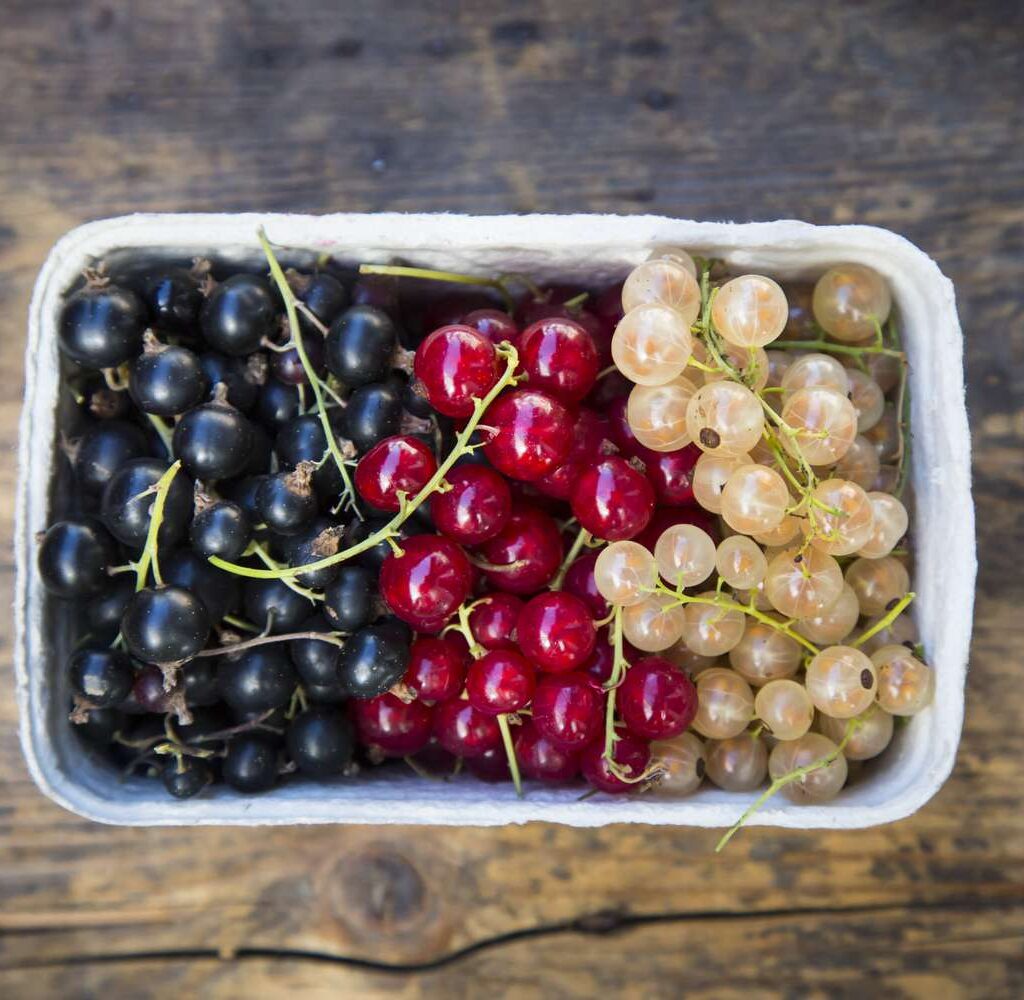
When it comes to berries, currants have long been celebrated for their rich flavor, vibrant colors, and impressive health benefits. Found in black, red, and white varieties, these tiny berries are a staple in jams, jellies, wines, and desserts across Europe and parts of Asia. But one question many might not know the answer to is — which country leads the world in currant production?
In this comprehensive article, we’ll explore which country is the largest currant producer in the world, dive into the history of currants, their uses, health benefits, global market trends, and the factors behind the top producer’s success.
What Are Currants?
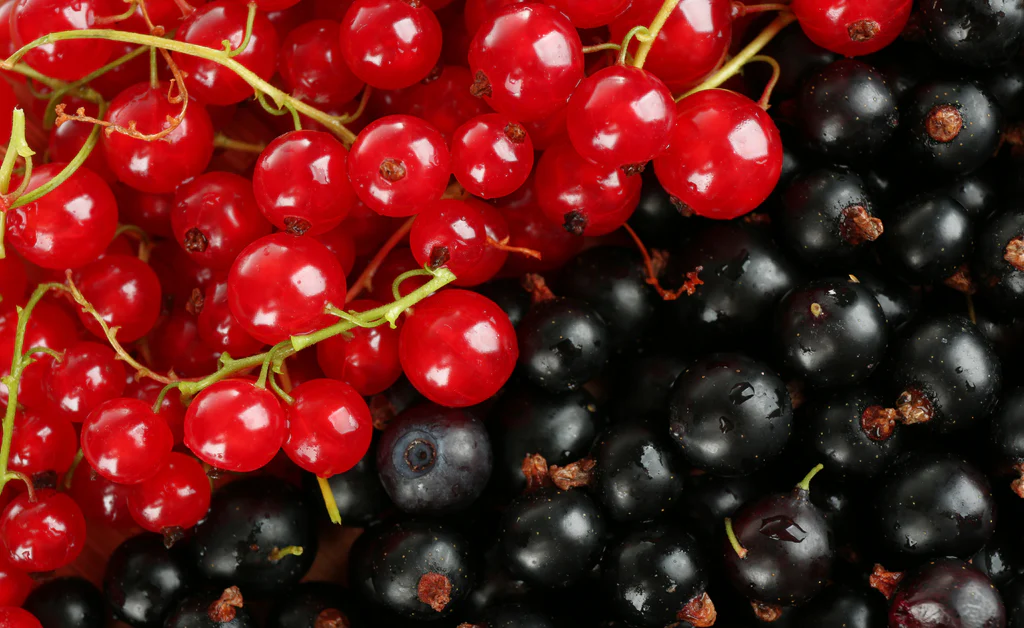

Currants are small berries that belong to the Ribes genus, native to the temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. They come in several varieties:
- Blackcurrants (Ribes nigrum)
- Redcurrants (Ribes rubrum)
- White currants (a color variant of redcurrants)
Known for their tart flavor and high vitamin C content, currants have been a vital part of European kitchens and traditional medicine for centuries.
Which Country Is the Largest Currant Producer in the World?
Russia holds the title as the largest currant producer in the world.
Key Production Stats:
- Annual Production: Approximately 156,000 metric tons
- Main Varieties Grown: Predominantly blackcurrants, followed by red and white currants.
- Primary Growing Regions: Central, Northwestern, and Southern Russia.
Russia’s dominance in currant production is largely due to its vast land area, favorable climate for berry cultivation, and a long-standing cultural tradition of using currants in food and medicine.
Other Leading Currant Producing Countries
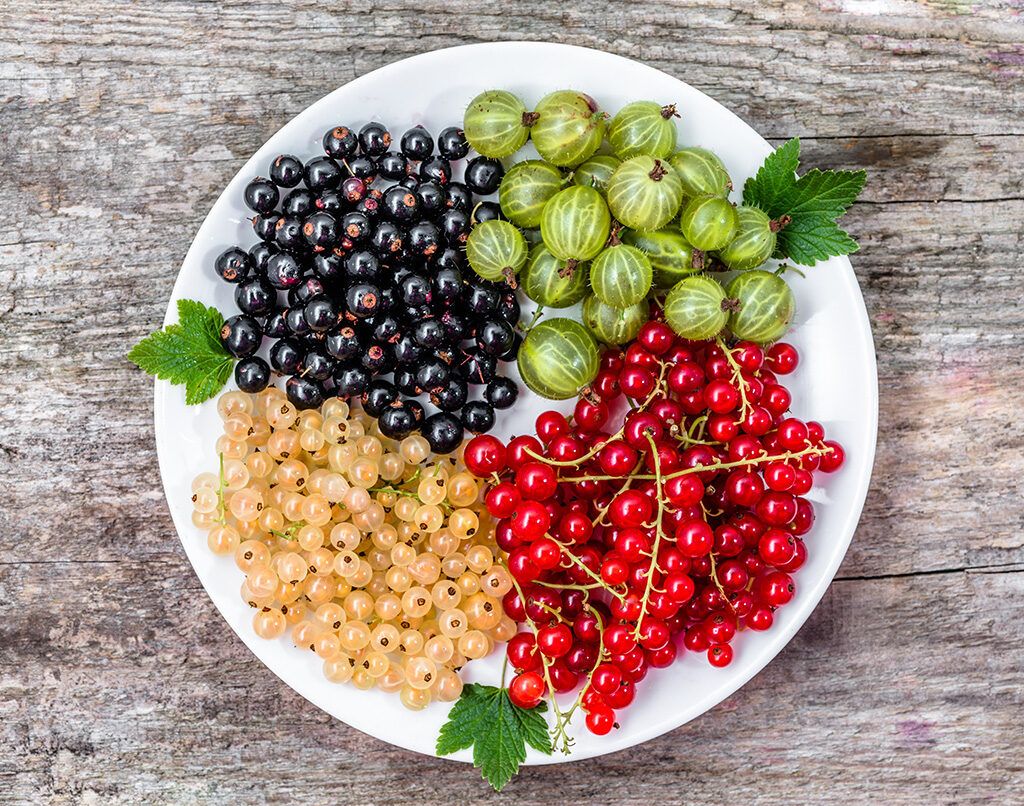

Though Russia leads globally, several other countries also have significant currant production:
Poland
- The world’s second-largest currant producer.
- Particularly known for high-quality blackcurrants, exported widely to European markets.
- Excellent climate and soil conditions make Poland a berry-farming hub.
Germany
- A historic producer of both black and red currants.
- Currants are an essential ingredient in German desserts, jams, and syrups.
Ukraine
- Large-scale currant farming, especially blackcurrants.
- Significant domestic and export markets.
United Kingdom
- Known for its premium blackcurrants.
- Famous for producing the fruit used in Ribena, one of the UK’s most popular fruit drinks.
Currant Farming: Varieties and Cultivation Practices
Currants thrive in cool, temperate climates with well-drained, fertile soil. The three main types of currants cultivated globally include:
Blackcurrants (Ribes nigrum)
- Dark purple to black berries.
- Rich in vitamin C, antioxidants, and anthocyanins.
- Popular for juices, jams, wines, and medicinal use.
Redcurrants (Ribes rubrum)
- Bright red berries.
- Tart flavor, often used in jellies, sauces, and desserts.
White Currants
- Pale, translucent berries.
- Mildly sweet and less acidic than redcurrants.
Key farming practices include:
- Pruning annually to improve yield and air circulation.
- Protecting plants from pests like aphids and diseases such as mildew.
- Irrigation during dry spells to maintain berry quality.
- Using organic and natural fertilizers for healthier produce.
Culinary and Commercial Uses of Currants
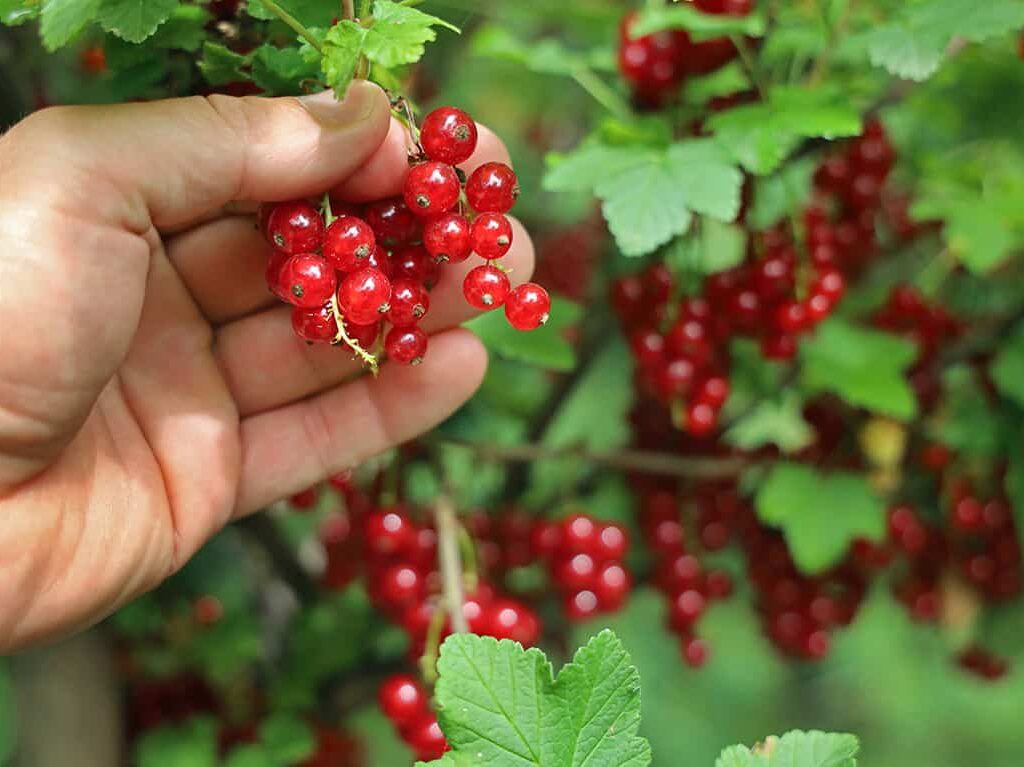

Currants are highly versatile and feature prominently in various culinary and commercial applications:
- Jams, jellies, and preserves
- Fruit syrups and juices
- Cakes, tarts, and pastries
- Wine and liqueurs (especially blackcurrant wines)
- Medicinal syrups for cough and cold remedies
- Health supplements, owing to their high antioxidant content
In Eastern Europe and Russia, currant berries are a staple in household recipes and are often preserved for winter use.
Health Benefits of Currants
Currants, particularly blackcurrants, are considered a superfood because of their impressive nutritional profile:
- Extremely high in Vitamin C: Boosts immunity and acts as a powerful antioxidant.
- Rich in Anthocyanins: Help fight inflammation and protect against oxidative stress.
- Good for Heart Health: May help reduce blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
- Improves Eye Health: Blackcurrants contain compounds that may protect against vision loss.
- Aids Digestion: High fiber content improves gut health.
- Supports Skin and Hair Health: Antioxidants and vitamins promote healthy skin and hair.
Global Currant Market Trends

The global demand for currants has steadily increased in recent years, driven by growing health awareness and the popularity of superfoods.
Key market trends include:
- Rising demand for organic currants in the EU and North America.
- Growth in the health supplement industry, with currant extracts used for immunity-boosting products.
- Increased use in functional beverages and natural colorants.
- Expansion of currant-based food products in gourmet and health-conscious markets.
Why Is Russia the Largest Currant Producer?
Several factors contribute to Russia’s position as the global leader in currant production:
- Vast Agricultural Land: Russia has enormous tracts of land suitable for berry farming.
- Favorable Climate: The cool, temperate climate is ideal for currant cultivation.
- Cultural Preference: Currants have deep roots in Russian culinary and folk medicine traditions.
- Strong Domestic Demand: Used in teas, jams, desserts, and natural remedies.
- Government and Private Investment: Berry farming is supported in several regions through agricultural initiatives.
Fun Facts About Currants

- Currants are banned in several U.S. states because they can harbor a disease harmful to pine trees known as white pine blister rust.
- Blackcurrant leaves are often used to flavor herbal teas.
- In medieval Europe, currants were considered a medicinal berry before gaining popularity as a dessert ingredient.
- Ribena, the famous British blackcurrant drink, was created during World War II when citrus imports were restricted.
Challenges in Currant Farming
Despite its popularity, currant farming presents some challenges:
- Susceptibility to Mildew and Pests: Regular pruning and organic treatments are necessary.
- Short Shelf Life: Fresh currants spoil quickly, limiting export potential without processing.
- Market Volatility: Prices fluctuate based on harvest volumes and export demand.
- Climate Change Impact: Unpredictable weather patterns affect yields.
Advancements in disease-resistant cultivars and improved farming techniques are helping overcome these challenges.
Conclusion
In summary, Russia proudly holds the title of the largest currant producer in the world, thanks to its ideal climate, vast land resources, and a deep cultural affinity for currants in food and medicine. Following closely behind are Poland, Germany, Ukraine, and the UK, each contributing significantly to the global currant market.
With the rise of health-conscious eating and the growing popularity of functional foods, the global demand for currants — especially organic and processed products — is expected to continue its upward trend.
Whether enjoyed fresh, in preserves, or as a rich, tangy addition to desserts and health products, currants remain one of the world’s most valued and versatile berries.
FAQs
Q: Which country grows the most currants globally?
A: Russia is the largest currant producer in the world.
Q: Are currants good for your health?
A: Yes — currants are rich in vitamin C, antioxidants, and dietary fiber, offering numerous health benefits.
Q: What are the different types of currants?
A: The main types are blackcurrants, redcurrants, and white currants.
Q: Can currants be grown in warmer climates?
A: Currants thrive in cool, temperate climates. Warmer regions require shaded areas and irrigation.




Leave A Comment