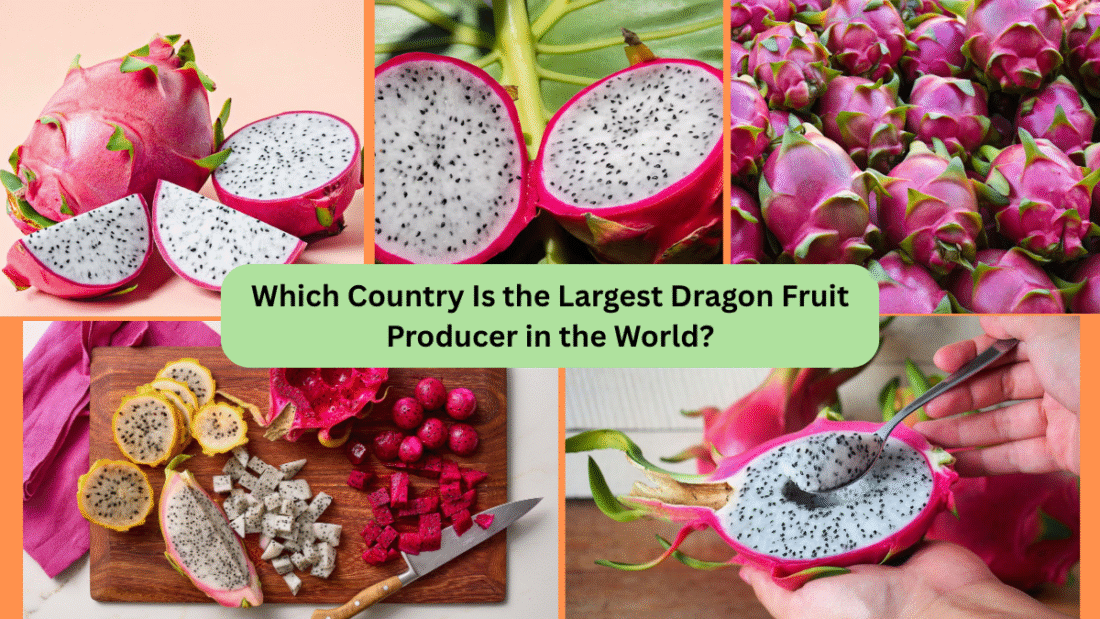
Dragon fruit, also known as pitaya or pitahaya, is one of the most exotic and visually captivating fruits in the world. With its vibrant pink or yellow skin, scaly texture, and speckled white or red flesh, dragon fruit has become increasingly popular for its health benefits, refreshing taste, and stunning appearance. But have you ever wondered which country leads the world in producing this tropical treasure?
Let’s dive deep into the vibrant world of dragon fruit cultivation and discover which nation tops the chart as the largest producer of dragon fruit in the world.
Global Overview of Dragon Fruit Production
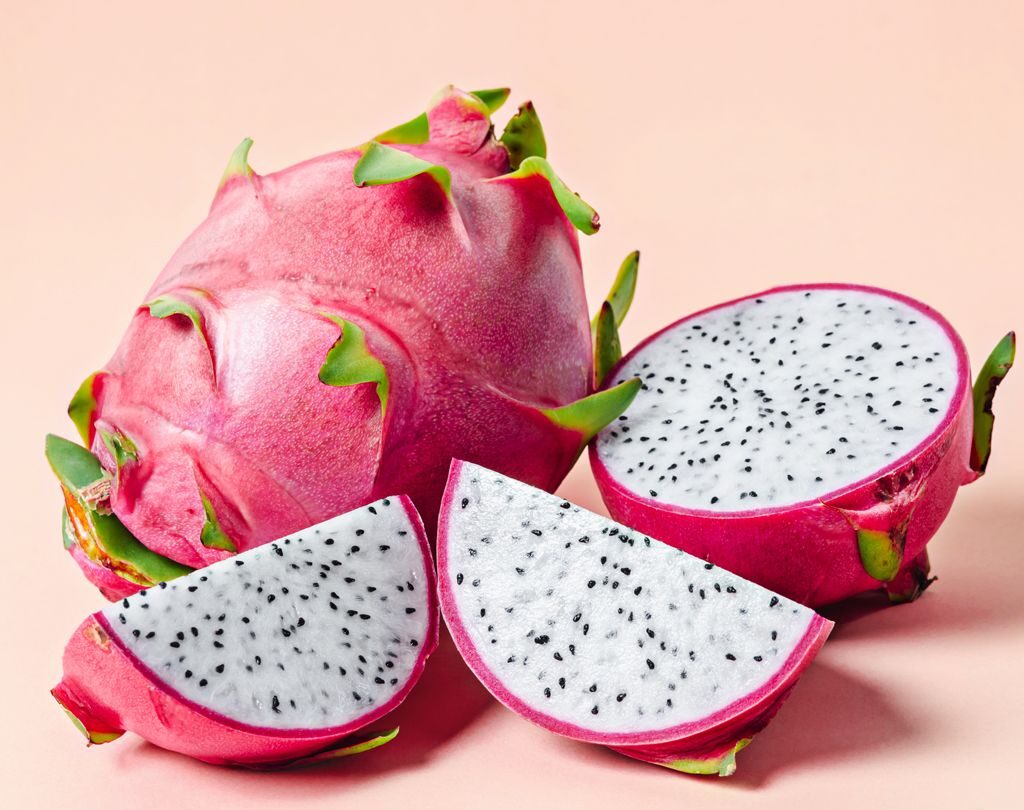

Dragon fruit belongs to the cactus family (Cactaceae), and it thrives in tropical and subtropical climates. Native to Central America, it was introduced to Asia in the early 19th century and has since gained enormous popularity, especially in countries with suitable climates.
Today, dragon fruit is commercially grown in several parts of the world, including:
- Vietnam
- Thailand
- Malaysia
- Philippines
- China
- India
- Nicaragua
- Colombia
- Israel
- Australia
Among these, Vietnam has emerged as the undisputed global leader in dragon fruit production.
Vietnam – The World’s Largest Dragon Fruit Producer
Production Volume & Global Share
Vietnam is the largest producer and exporter of dragon fruit globally, accounting for over 50% of the world’s supply. According to recent statistics from Vietnam’s Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development, the country produces over 1.3 million tons of dragon fruit annually. The majority of this production is exported to more than 40 countries, including China, the United States, India, the European Union, and the Middle East.
Major Growing Regions
Dragon fruit cultivation in Vietnam is primarily concentrated in the southern and central provinces, particularly:
- Bình Thuận Province – Known as the “dragon fruit capital” of Vietnam, this area accounts for more than 60% of the country’s production.
- Long An Province
- Tiền Giang Province
These provinces provide the ideal conditions for dragon fruit farming — warm temperatures, sandy soil, and low rainfall during flowering and fruiting seasons.
Farming Practices & Innovation
Vietnamese farmers have developed specialized techniques for growing dragon fruit on a large scale, including:
- Nighttime lighting: To stimulate flowering and allow for multiple harvests per year, LED or incandescent lights are used.
- Trellis systems: Tall concrete posts support the climbing cactus vines, maximizing space and sunlight exposure.
- Organic farming: There’s a growing shift toward sustainable and organic farming to meet global food safety standards.
Export Dominance
Vietnam exports over 80% of its dragon fruit production, with the biggest market being China, followed by:
- India
- Thailand
- Indonesia
- The United States
- Japan
- South Korea
- Netherlands
Vietnam has been proactive in meeting international standards, investing in post-harvest technologies, cold chain logistics, and GAP (Good Agricultural Practices) certifications.
China – A Rapidly Growing Competitor

Although Vietnam is the top producer, China is rapidly expanding its domestic dragon fruit farming and may soon become a serious contender. In the past decade, dragon fruit cultivation in Guangxi, Hainan, Guangdong, and Yunnan has grown substantially.
China currently produces around 800,000 to 1 million tons of dragon fruit annually. With strong government support and massive land areas available, Chinese farmers are embracing modern farming methods and high-yield varieties to boost production.
However, a significant portion of the dragon fruit consumed in China still comes from Vietnamese imports, as Chinese production hasn’t yet surpassed domestic demand.
Thailand – A Consistent Contributor
Thailand is also a significant player in the dragon fruit industry. It produces approximately 200,000 to 250,000 tons annually, primarily for domestic consumption and small-scale exports to neighboring countries.
The Thai government has encouraged the cultivation of red-fleshed varieties due to their popularity and antioxidant properties. Thailand is also exploring value-added products like dragon fruit juice, snacks, and cosmetics to boost its market presence.
India – A Rising Star

India, traditionally not associated with dragon fruit, is emerging as an important player. In recent years, Indian farmers have started cultivating the fruit in states like:
- Maharashtra
- Karnataka
- Gujarat
- Andhra Pradesh
- Odisha
India produces over 70,000 tons of dragon fruit annually (and growing), and the government has recognized its potential through initiatives like the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH) and One District One Product (ODOP).
India’s vast domestic market and increasing consumer awareness are driving demand. Though exports are still minimal, India could become a major global supplier in the future.
Why Is Dragon Fruit So Popular?

Dragon fruit has captured global attention due to a variety of factors:
Health Benefits
- Rich in antioxidants like vitamin C, betalains, and carotenoids
- Boosts immune system and promotes gut health with high fiber content
- Low calorie and hydrating, making it ideal for weight-conscious diets
- May help regulate blood sugar and cholesterol levels
Culinary Versatility
From smoothie bowls and salads to sorbets and cocktails, dragon fruit is widely used in:
- Beverages
- Desserts
- Functional foods
- Skincare and cosmetics
Its bright colors and mild sweetness make it a favorite among chefs and food enthusiasts.
Challenges Facing Dragon Fruit Producers

Despite the booming market, there are challenges producers must navigate:
Disease & Pests
Fungal diseases like anthracnose and pests such as mealybugs can damage crops.
Climate Sensitivity
Dragon fruit requires consistent warmth and low humidity during flowering — unseasonal rains or cold spells can reduce yields.
Trade Barriers & Quality Control
Stringent import regulations, especially in the EU and USA, mean farmers must meet high standards for pesticide use and hygiene.
Market Fluctuations
Prices are highly volatile and influenced by international demand, competition, and supply chain logistics.
Final Thoughts
So, which country is the largest dragon fruit producer in the world? The clear answer is:
Vietnam — with over 1.3 million tons produced annually and a robust export infrastructure.
Vietnam has set the global benchmark in dragon fruit cultivation, innovation, and international trade. However, countries like China, India, and Thailand are fast catching up, creating a dynamic and competitive global market.
As dragon fruit continues to gain popularity worldwide, it presents exciting opportunities for farmers, exporters, and consumers alike. Whether you’re a health-conscious eater or a tropical fruit lover, dragon fruit is more than just a pretty face — it’s a symbol of how agriculture can evolve to meet modern global tastes.