The Gac fruit (Momordica cochinchinensis) is a rare and vibrant tropical fruit native to Southeast Asia, cherished for its rich nutritional value, bright orange-red hue, and significant health benefits. Also known as “baby jackfruit” or “spiny bitter gourd,” this fruit has garnered attention in both traditional medicine and modern wellness markets. But among all the nations cultivating this exotic fruit, one country reigns supreme. In this detailed article, we’ll discover which country is the largest producer of Gac fruit in the world, the reasons for its dominance, and the broader cultural and economic importance of this little-known superfruit.
What is Gac Fruit?
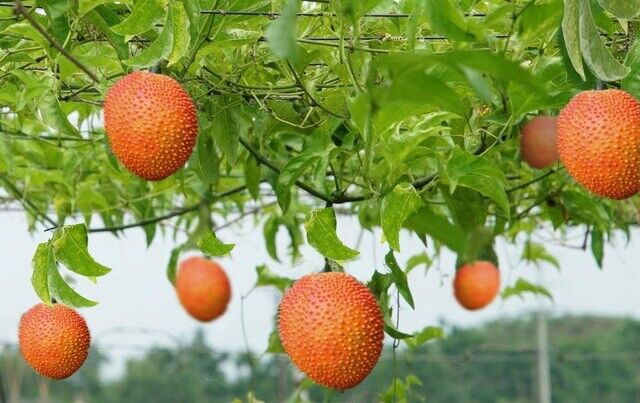

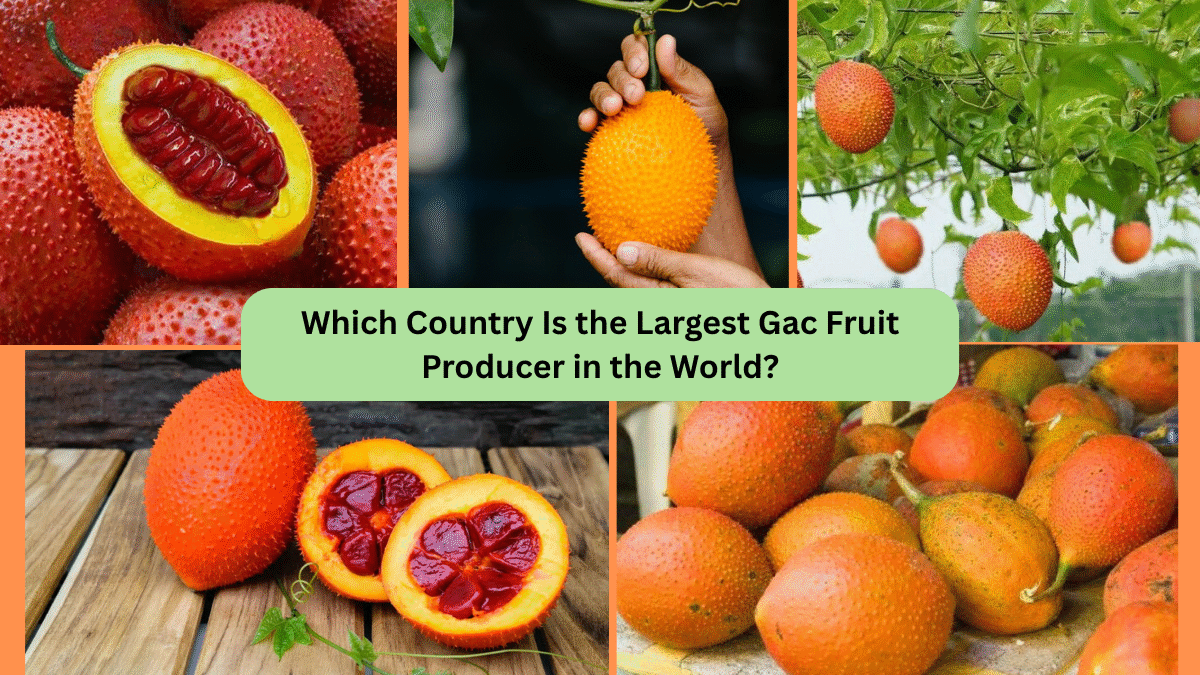
Gac fruit is a perennial vine that produces round or oval fruits with spiny skin and intensely colored pulp. It’s celebrated for its exceptionally high content of carotenoids, particularly lycopene and beta-carotene, both potent antioxidants.
Scientific Name: Momordica cochinchinensis
Common Names: Gac, Baby Jackfruit, Spiny Bitter Gourd, Red Melon
Historical and Cultural Importance
Gac has been cultivated for centuries in Southeast Asia for both culinary and medicinal purposes.
- In Vietnam: It’s a traditional ingredient in festive dishes like xôi gấc (red sticky rice), served at weddings and Lunar New Year celebrations.
- In Traditional Medicine: Used to improve vision, boost immunity, and support cardiovascular health.
- In Rural Communities: The fruit and its seeds are believed to possess healing properties.
The Largest Gac Fruit Producer in the World: Vietnam
Vietnam is the world’s largest producer of Gac fruit.
Why Vietnam Leads Gac Production
1. Indigenous Origin and Ideal Climate:
Vietnam’s tropical monsoon climate, fertile soil, and widespread indigenous growth of Gac vines make it the ideal environment for this crop.
2. Deep Cultural Integration:
Gac is a staple in Vietnamese culinary and wellness traditions, ensuring strong domestic demand.
3. Expanding Commercial Cultivation:
Vietnam has increased commercial Gac plantations, particularly in the northern provinces such as Hanoi, Vinh Phuc, and Ninh Binh.
4. Research and Agricultural Support:
Vietnamese agricultural universities and research centers actively promote high-yield varieties and organic cultivation techniques.
5. Export-Oriented Production:
Vietnam has developed processing facilities for Gac oil, powders, and supplements, primarily exported to Japan, Korea, Australia, and the United States.
Production Statistics

- Vietnam accounts for over 75% of global Gac production.
- Northern provinces like Hanoi, Phu Tho, and Bac Giang are the largest producers.
- Vietnam processes Gac into oil, juice, puree, and functional supplements for both local and export markets.
Other Gac Producing Countries
While Vietnam dominates, Gac is also grown in:
- Thailand: Primarily for local culinary use.
- Laos and Cambodia: Limited cultivation in rural areas.
- China and Myanmar: Small-scale production.
- Australia: Niche farming for health markets.
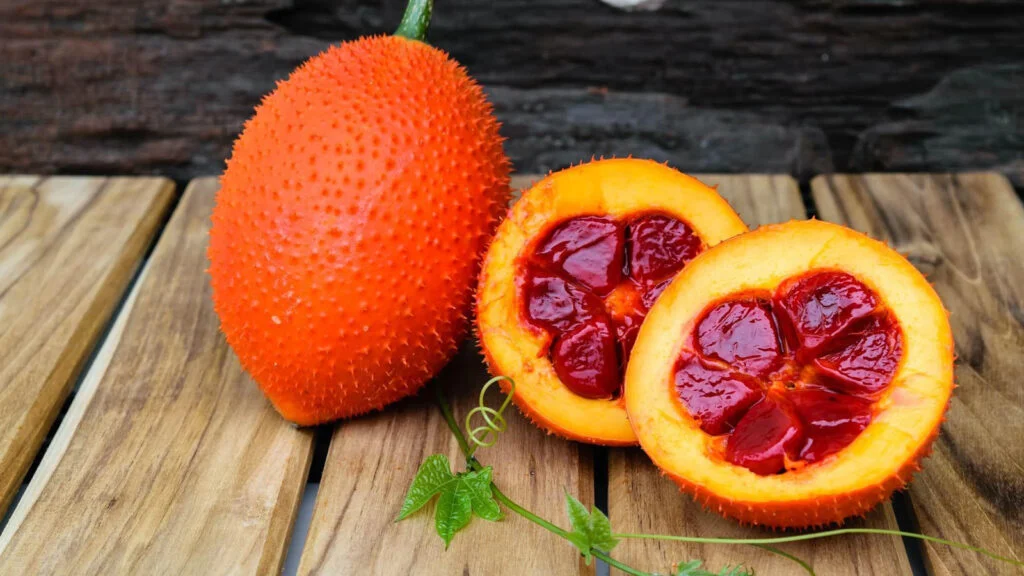
Nutritional and Medicinal Benefits
Gac is dubbed a “superfruit” because of its remarkable nutritional profile:
- Lycopene: 70 times more than tomatoes.
- Beta-Carotene: 10 times more than carrots.
- Vitamin E and C: Boost immunity and skin health.
- Omega Fatty Acids: Found in its seeds.
Health Benefits:
- Protects eye health and vision.
- Reduces inflammation.
- Strengthens immunity.
- Supports cardiovascular health.
- Promotes youthful skin and cellular protection.
Common Uses
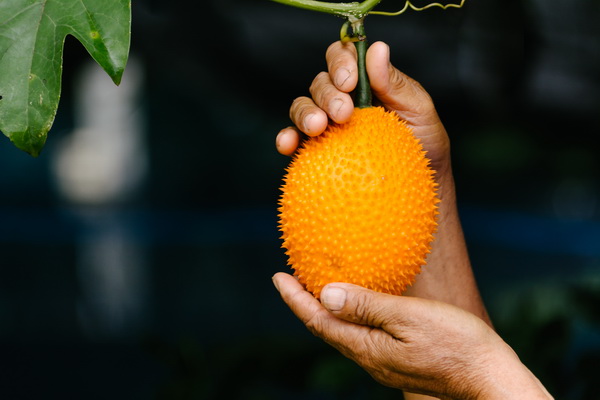

- Festive Dishes: Xôi gấc (red sticky rice).
- Juices and Smoothies: Combined with other tropical fruits.
- Dietary Supplements: Gac oil capsules.
- Skincare Products: Anti-aging creams and serums.
Economic Importance in Vietnam
- Rural Employment: Provides income for smallholder farmers.
- Export Revenue: Rising demand in wellness markets boosts exports.
- Agro-Processing Sector: Growth of Gac-based health and beauty products.
Challenges in Gac Production

- Seasonal Availability: Typically harvested once or twice a year.
- Perishability: Requires quick processing post-harvest.
- Limited Global Awareness: Still largely unknown outside Asia.
- Pest and Disease Susceptibility: Vulnerable to fungal infections.
Research and Innovations
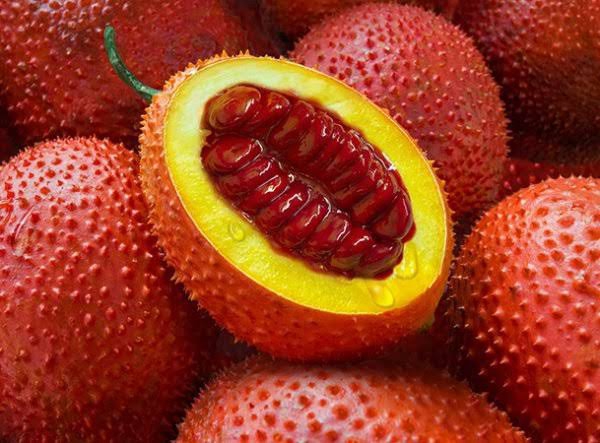

Vietnam is investing in:
- High-Yield Varieties: Such as Gac V6 and V7.
- Post-Harvest Technologies: Cold storage and drying.
- Functional Food Development: Incorporating Gac in beverages and nutraceuticals.
- Organic and Sustainable Farming: Supported by government programs.
Sustainability and Environmental Benefits
- Eco-Friendly Crop: Requires minimal chemical inputs.
- Agroforestry Potential: Can be grown alongside other fruit crops.
- Soil Conservation: Dense vines prevent erosion.
Future Growth and Global Trends
- Rising Demand for Natural Antioxidants: Especially lycopene-rich superfoods.
- Functional Foods and Beverages: Gac-based products gaining attention in Japan, South Korea, and Australia.
- Health and Beauty Markets: Growth of Gac-infused cosmetics.
- Agro-Tourism: Farm visits and Gac harvesting experiences.
Conclusion
Vietnam stands as the undisputed world leader in Gac fruit production, backed by ideal growing conditions, deep cultural roots, and a burgeoning health-focused market. As awareness of this remarkable superfruit spreads, Vietnam is well-positioned to capitalize on rising global demand for natural, antioxidant-rich products.
With continued innovation, sustainable practices, and strategic exports, Gac fruit is set to transition from a traditional delicacy to an international superfruit sensation—carrying the legacy of Vietnamese agriculture onto the global wellness stage.




Leave A Comment